Explore web search results related to this domain and discover relevant information.
Heart failure is often diagnosed after patients have already lost much of their function and quality of life, but emerging tools that noninvasively measure heart function may offer new ways to catch the disease sooner.
A recent study published in JACC: Advances tested one such tool, the FDA-cleared Vivio System, which estimates left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP), in more than 2000 patients at high risk for heart failure who were seen at three primary care centers.Nearly 40% of these patients, all of whom had diabetes, chronic kidney disease, or suspected heart failure, had elevated LVDEP, an indicator of heart failure. More than two thirds also reported symptoms, limitations, or impaired quality of life.Many heart failure diagnoses occur in the emergency room or inpatient setting, according to lead study author Omar Cantu-Martinez, MD, from Healthcare Institute for Innovations in Quality, University of Missouri-Kansas City, and Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Missouri.Experts agree that earlier detection of heart failure has the potential to lower hospitalization and mortality rates. “Our goal is to catch heart failure before it catches our patients off guard,” Cantu-Martinez said.

The first sign of heart failure often presents as breathing difficulties. The condition leads to shortness of breath that occurs after performing typical daily tasks such as stair climbing or walking. The inability to breathe properly also occurs when you rest, or when you lie flat in bed flat.
Your lungs will experience fluid accumulation because of heart weakness, which restricts your breathing ability. Some people use pillow elevation during sleep to enhance their breathing comfort. Heart failure symptoms include unexpected nighttime breathing emergencies that require immediate medical assistance.The swelling begins in your feet and ankles before it progresses to your legs during the course of a day. The swelling in your abdomen creates discomfort and bloating sensations. Your heart failure symptoms become apparent through tightness in your shoes, rings and unexpected weight gain that does not result from dietary changes.Fatigue serves as a primary indicator, which signals the onset of heart failure. The insufficient blood circulation from the heart results in decreased oxygen and nutrient delivery to your muscles and organs. The lack of sufficient blood circulation through your heart, leads to chronic fatigue that persists even when you rest.A persistent cough that produces white or pink-tinged mucus, may indicate heart failure as its underlying cause. The buildup of fluid in lung tissue known as pulmonary congestion, creates airway irritation which results in this condition. Wheezing together with a rattling sound during breathing, occurs frequently in patients.
Emergency department physicians in all Kaiser Permanente Northern California hospitals can now use a risk tool to help them evaluate patients with heart failure who develop new or worsening symptoms. The computerized risk calculator, which
The tool, called STRIDE-HF (Systematic Tool for Risk Identification and Decision-making in Emergency Heart Failure), became available in all Kaiser Permanente Northern California hospitals after a series of studies showed it was safe and effective.The most recent study to support its use was published in June in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology: Heart Failure.People who are experiencing heart-failure symptoms, including shortness of breath, weakness, fatigue, or coughing and wheezing, will often go to the emergency department for care.Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump as much blood as the body needs. The condition, which worsen over time, can cause damage to the kidneys and other organs.


A joint statement by the American Society for Preventive Cardiology (ASPC) and the Heart Failure Society of America (HFSA), published on August 13, 2025, shifts the focus of heart failure from recovery to prevention for the first time.
In the sixth episode of a 7-part HCPLive Special Report, moderator James Januzzi, MD, is joined by Martha Gulati, MD, MS, and Anu Lala, MD, to discuss the urgent need to bridge the gap between prevention and heart failure care.Lala outlines three key priorities for improving prevention in women at risk for heart failure: early identification, closing implementation gaps, and driving policy and payment reform. She stresses that many existing risk tools are based on male populations, which leads to underrecognition of women’s risks.She also draws attention to peripartum cardiomyopathy and Takotsubo syndrome—forms of heart failure disproportionately affecting women—that are often underdiagnosed and lack effective preventive strategies.Both experts agree that greater inclusion of women in clinical trials is essential for understanding how therapies apply across sexes. Gulati notes that intentional enrollment efforts have already begun to improve representation in heart failure research, shifting from historically poor female participation toward more balanced studies.
Heart failure is a condition that occurs when your heart can't pump enough blood for your body's needs. Learn about the symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatments for heart failure.
Heart failure, also known as congestive heart failure, is a condition that develops when your heart doesn’t pump enough blood for your body’s needs. This can happen if your heart can’t fill up with enough blood. It can also happen when your heart is too weak to pump properly.Heart failure can develop suddenly (the acute kind) or over time as your heart gets weaker (the chronic kind). It can affect one or both sides of your heart. Left-sided and right-sided heart failure may have different causes. Most often, heart failure is caused by another medical condition that damages your heart.Your doctor will diagnose heart failure based on your medical and family history, a physical exam, and results from imaging and blood tests. Currently, heart failure is a serious condition that has no cure. However, treatment such as healthy lifestyle changes, medicines, some devices, and procedures can help many people have a higher quality of life.The term "heart failure" does not mean that your heart has stopped.


The research, presented at a major heart conference in Madrid last month and published in The New England Journal of Medicine, found that people who boosted their potassium levels were less likely to be hospitalized with heart rhythm issues or heart failure or to die from related complications.
Among the participants in the first group, around 23% experienced a medical event such as a dangerously fast heart rhythm, treatment by a defibrillator (either a shock or pacing), an unplanned hospital stay for heart rhythm problems or heart failure, or death from any cause.The researchers concluded that in patients with cardiovascular disease who had an ICD and were at high risk for ventricular arrhythmias, increasing plasma potassium levels led to a "significantly lower risk of appropriate ICD therapy, unplanned hospitalization for arrhythmia or heart failure, or death from any cause than standard care."A new study of 1,200 patients shows that higher potassium levels reduce heart failure hospitalizations and arrhythmias in high-risk cardiovascular patients with ICDs.Copenhagen University Hospital research finds that increasing potassium levels significantly lowers death risk and heart complications in cardiac patients.
Heart failure is a serious condition. The heart cannot pump enough blood and oxygen.
Heart failure happens when the heart cannot pump enough blood and oxygen to support other organs in your body.Certain medical conditions can increase your risk for heart failure.Heart failure is a serious condition, but it does not mean that the heart has stopped beating.Heart failure cost the nation an estimated $30.7 billion in 2012.


Heart failure often starts subtly, with symptoms like fatigue, breathlessness, and swelling easily dismissed as stress or aging. Recognizing these early signs, summarized by the FACES acronym (Fatigue, Activity limitations, Congestion, Edema, Shortness of breath), is crucial.
But what if it's quietly struggling before you even notice?Your heart might be sending distress signals, and they’re whispering, not shouting. Heart failure, a progressive condition where the heart doesn’t pump well, often begins with soft clues that get missed: random fatigue, mild breathlessness, or even foggy thinking.These early signs are slippery; they’re easy to write off as “just stress” or “getting older.” But what starts small can grow serious fast.Renowned cardiologist Dmitry Yaranov, MD, echoes the same sentiment. As per Yaranov, heart failure often begins with subtle, easily dismissed symptoms – fatigue, breathlessness when lying down, or a persistent cough that seems harmless.To make it simpler and easier to recognize, Harvard Health introduced the FACES acronym to describe early heart failure symptoms: Fatigue, Activity limitations, Congestion, Edema, and Shortness of breath. Here’s what each of these might feel like:Fatigue and activity limitationFatigue: More than just feeling tired, it’s a heavy exhaustion that lingers even after rest or a full night’s sleep.Which conditions are those?High blood pressureDiabetesObesityCoronary artery diseaseA prior heart attackLifestyle risks like smoking, poor diet, and inactivityHeart failure often develops gradually, which makes early detection and lifestyle changes a powerful prevention tool.
Weight loss drugs could help improve health outcomes in people with heart failure.
Researchers report that the weight loss drugs semaglutide and tirzepatide can reduce the risk of hospitalization and death by 40% in people with a common type of heart failure.Researchers noted that their study supports the results of smaller, earlier studies on GLP-1 drugs and heart failure.Experts said the new research opens up the possibility of new treatments for people with this form of heart failure.“These findings complement early results from small clinical trials and support the use of semaglutide and tirzepatide in patients with cardiometabolic heart failure with preserved ejection fraction,” the authors wrote.
Discover how early palliative care improves quality of life and heart function in chronic heart failure patients, particularly those with NYHA grades 2 and 3.
Background: Chronic heart failure (HF) is a life limiting illness that can greatly affect a persons’ quality of life by limiting mobility, causing pain and dyspnea, frequent hospitalizations, and psychological distress. As the disease progresses, their needs increase and change.Source: Pan L, Qiao L, Zhang Y, et al. Effectiveness of timely implementation of palliative care on the well-being of patients with chronic heart failure. J Palliat Care. 2024;39(4):282-288.Design and Participants: This was a case-control study from January 2018-December 2020. One hundred and eighty participants were >60 years old, were diagnosed with chronic HF with a New York Heart Association (NYHA) grade 1-3, were cognitively intact and had no other life limiting illnesses such as neurological disease, obesity, or cancer.Bottom Line: Chronic HF significantly impacts a patient’s quality of life and their engagement in their health. Early palliative care interventions in patients with NYHA grades 2 and 3 significantly improve their quality of life and self-care, resulting in improved heart function.

Read more about heart failure and planning for the end of life. ... To find out more, or to support British Heart Foundation’s work, please visit www.bhf.org.uk. You can speak to one of our cardiac nurses by calling our helpline on 0808 802 1234 (freephone), Monday to Friday, 9am to 5pm.
The stages of heart failure are a classification system doctors use to describe how severe your condition is in terms of your symptoms.Being told you have heart failure can feel like a lot to take in.Heart failure does not mean your heart has stopped working.There are different causes of heart failure, such as a heart attack, high blood pressure, or because of other heart conditions.
Congestive heart failure (also called heart failure) is a serious condition in which the heart doesn’t pump blood as efficiently as it should. Despite its name, heart failure doesn’t mean that the heart has literally failed or is about to stop working. Rather, it means that the heart muscle ...
Congestive heart failure (also called heart failure) is a serious condition in which the heart doesn’t pump blood as efficiently as it should. Despite its name, heart failure doesn’t mean that the heart has literally failed or is about to stop working. Rather, it means that the heart muscle has become less able to contract over time or has a mechanical problem that limits its ability to fill with blood.The heart beats faster to take less time for refilling after it contracts—but over the long run, less blood circulates, and the extra effort can cause heart palpitations. The heart also enlarges a bit to make room for the blood. The lungs fill with fluid, causing shortness of breath. The kidneys, when they don’t receive enough blood, begin to retain water and sodium, which can lead to kidney failure.More than 5 million people in the United States have congestive heart failure. It’s the most common diagnosis in hospitalized patients over age 65. One in nine deaths has heart failure as a contributing cause.Ongoing care and adherence to prescribed medications, such as statin drugs to treat high cholesterol, can make a big difference. Research shows that a major portion of the long-term benefit of statin therapy is in the prevention of heart failure by way of preventing heart attacks and coronary events that lead to it.
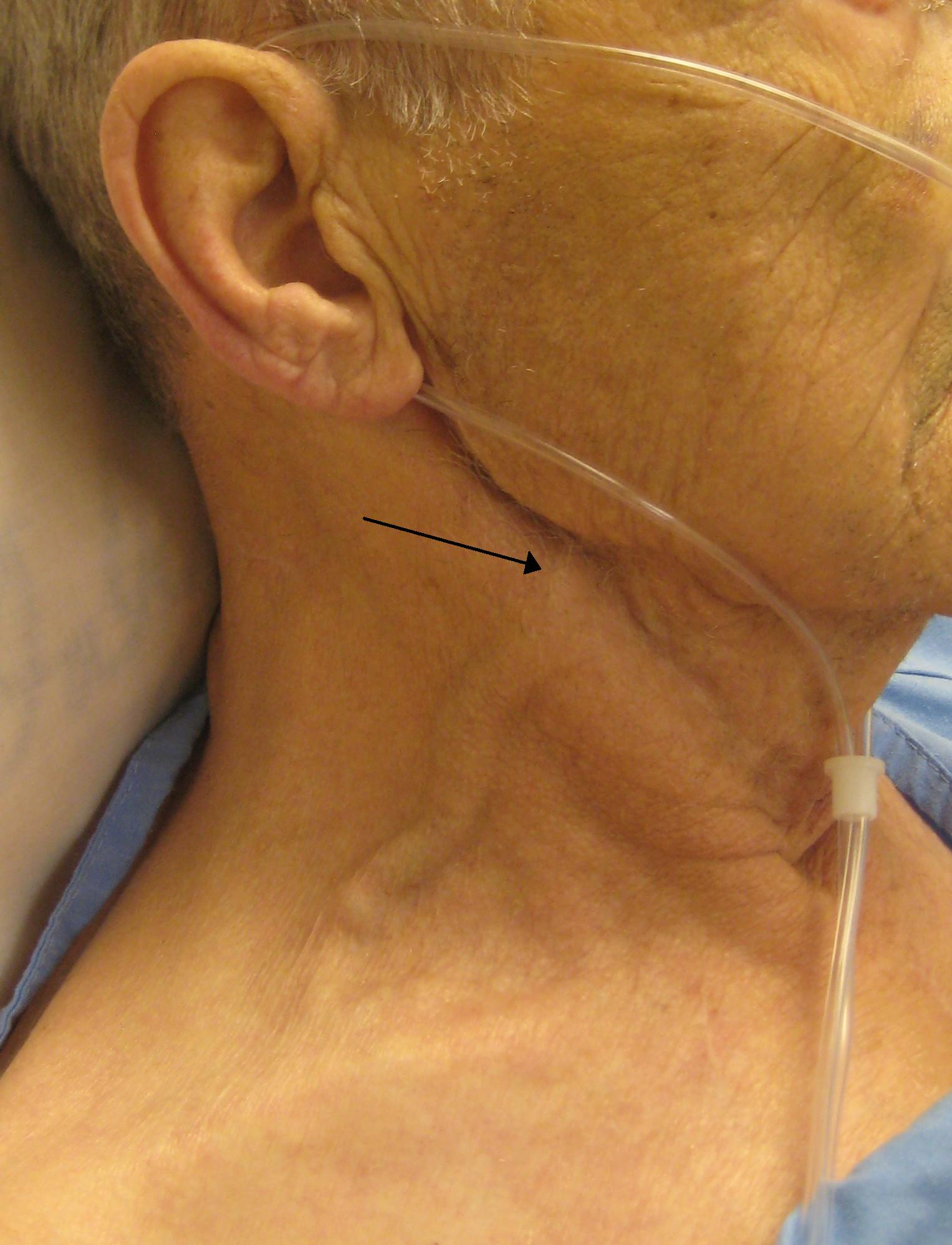
Heart failure develops when the heart, via an abnormality of cardiac function (detectable or not), fails to pump blood at a rate commensurate with the requirements of the metabolizing tissues or is able to do so only with an elevated diastolic filling pressure. See the image below.
Heart failure is the pathophysiologic state in which the heart, via an abnormality of cardiac function (detectable or not), fails to pump blood at a rate commensurate with the requirements of the metabolizing tissues or is able to do so only with an elevated filling pressure.Heart failure always causes circulatory failure, but the converse is not necessarily the case, because various noncardiac conditions (eg, hypovolemic shock, septic shock) can produce circulatory failure in the presence of normal, modestly impaired, or even supranormal cardiac function.Heart Failure. A 28-year-old woman presented with acute heart failure secondary to chronic hypertension. The enlarged cardiac silhouette on this anteroposterior (AP) radiograph is caused by acute heart failure due to the effects of chronic high blood pressure on the left ventricle.Breathlessness is a cardinal symptom of left ventricular (LV) failure that may manifest with progressively increasing severity. Heart failure can be classified according to a variety of factors.
Heart failure (HF), as defined by the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA), is a complex clinical syndrome that results from any structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood. HF is a common disorder worldwide with a ...
Heart failure (HF), as defined by the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA), is a complex clinical syndrome that results from any structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood. HF is a common disorder worldwide with a high morbidity and mortality rate.Every attempt should be made to identify causative factors to help guide treatment strategies. The etiologies can be broadly classified as intrinsic heart disease and pathologies that are infiltrative, congenital, valvular, myocarditis-related, high-output failure, and secondary to systemic disease.[3][4] These classifications have significant overlap.Obesity is a leading cause of CHF in patients younger than 40 years, according to the "Candesartan in Heart Failure Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and Morbidity" (the CHARM study). The "obesity paradox" described elsewhere has significant study flaws and is derived from older data.While patients with acute HF present with overt respiratory distress, orthopnea, and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, patients with chronic heart failure tend to curtail their physical activity; hence, symptoms may be obscured.

The right sided chamber gets blood from body organs and pumps blood to the lungs to get oxygen. The left sided chambers gets this oxygen-rich blood from lungs and pumps it to the rest of the body. In heart failure, this process of circulation of blood across cardiovascular system becomes deficient.
Most heart failure develops slowly over time due to multiple causes but it can occur suddenly also : •Coronary artery disease (blockages in the heart’s arteries) and heart attacks if not treated in appropriate time •Uncontrolled high blood pressure •Diabetes • valvular heart diseases •Irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) •Alcohol abuse, smoking •Viral infections of the heart muscle Other serious illnesses such as kidney disease or thyroid problems Overdose of medications Chronic lung and liver diseases Congestive heart failure is a term used when fluid buildup (congestion) causes swelling of body and breathing difficulty.Common medicines include diuretics, ARNI, beta blockers, SGLT2 inhibitors, Vericiguat. There are advanced heart failure therapies available for certain subset of people Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD) An ICD is a small device placed under the skin of your chest, connected to your heart with thin wires.Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) If your heart’s chambers are out of sync with each other this therapy is useful. It uses a pacemaker with extra wires to coordinate the pumping of the heart’s lower chambers.Not everyone needs CRT, but for people with certain types of heart failure, it can be life-changing.It helps blood flow to the rest of your body and can be used as a long-term solution or as a bridge while waiting for a heart transplant. Heart Transplant In rare cases when all other treatments fail and the heart is so damaged that it cannot support life, a heart transplant is considered.
Heart failure, or congestive heart failure (CHF), means the heart can't pump enough blood. Learn about the signs, symptoms and causes.
But in most cases, heart failure develops slowly from long-term medical conditions. ... Over time, left-sided heart failure can lead to right-sided heart failure.Heart failure can happen at any age. It happens to both men and women, but men often develop it at a younger age than women. Your chance of developing heart failure increases if: You're 65 years old or older. Aging can weaken and stiffen your heart muscle.Your family health history includes relatives who have or have had heart failure. You have changes in your genes that affect your heart tissue.African Americans are more likely to develop heart failure and have more serious cases at younger ages than people of other races. Factors such as stigma, discrimination, income, education, and geographic region can also affect their risk of heart failure. The symptoms of heart failure depend on which side of your heart is affected and how serious your condition has become.

Learn about this chronic disease that needs lifelong management. Find out what treatments help you live longer and may even strengthen your heart.

Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (known as HFpEF), is the most common kind of heart failure, affecting millions globally. The heart still pumps, it just can't relax and fill appropriately. Think of it like a stiff balloon that won't stretch, blood backs up, pressure builds, and ...
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (known as HFpEF), is the most common kind of heart failure, affecting millions globally. The heart still pumps, it just can't relax and fill appropriately. Think of it like a stiff balloon that won't stretch, blood backs up, pressure builds, and breathing becomes a struggle.The Adipokine Hypothesis emphasizes the therapeutic potential of targeting dysfunctional fat tissue, not just to reduce its volume, but to restore its beneficial signaling profile. Several FDA-approved drugs for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) already act on this pathway, yet remain underutilized in clinical practice.Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (known as HFpEF), is the most common kind of heart failure, affecting millions globally. The heart still pumps, it just can't relax and fill appropriately. Think of it like a stiff balloon that won't stretch, blood backs up, pressure builds, and…Discover how internal fat and adipokines impact HFpEF, offering new treatment paths for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
The American Heart Association explains heart failure (HF), sometimes called congestive heart failure (CHF), as a chronic, progressive condition in which the heart muscle is unable to pump enough blood through the heart to meet the body's needs for blood and oxygen. Learn more.
Heart failure (sometimes called congestive heart failure) is a chronic, progressive condition in which the heart muscle is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs for blood and oxygen.Your body depends on the heart’s pumping action to deliver oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood to the body’s cells. With heart failure, the weakened heart can’t supply the cells with enough blood. This results in fatigue and shortness of breath. Some people have excessive coughing.Heart failure is a condition in which the heart muscle can’t pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs for blood and oxygen. Basically, the heart can’t keep up with its workload. HF is a lifelong condition, but you may have HF remission with treatment and healthy lifestyle changes.This creates increased blood volume, which helps maintain blood pressure and allows the heart to pump stronger. But over time, this extra volume can overwork the heart, making heart failure worse. These short-term measures mask heart failure, but they don’t solve it.

Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to fill with and pump blood. Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF typically presents with shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, ...
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF typically presents with shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and bilateral leg swelling. The severity of the heart failure is mainly decided based on ejection fraction and also measured by the severity of symptoms.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering the structure or the function of the heart or in some cases both.There are different types of heart failure: right-sided heart failure, which affects the right heart, left-sided heart failure, which affects the left heart, and biventricular heart failure, which affects both sides of the heart. Left-sided heart failure may be present with a reduced reduced ejection fraction or with a preserved ejection fraction.Overall, heart failure affects about 2% of adults, and more than 10% of those over the age of 70. Rates are predicted to increase. The risk of death in the first year after diagnosis is about 35%, while the risk of death in the second year is less than 10% in those still alive. The risk of death is comparable to that of some cancers. In the United Kingdom, the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times in Egypt; it is mentioned in the Ebers Papyrus around 1550 BCE.Most of the visible signs of heart failure are the result of this fluid accumulation (edema) and the adjective congestion is added to the definition of heart failure. Impaired ejection can lead to inadequate blood flow to the body tissues, resulting in ischemia. Congestive heart failure is a pathophysiological condition in which the heart's output is insufficient to meet the needs of the body and lungs.